
ERP ย่อมาจาก Enterprise Resource Planning หรือการวางแผนทรัพยากรองค์กร ซึ่งเป็นระบบซอฟต์แวร์หลักสำหรับการจัดการการดำเนินงานทางธุรกิจ ตามข้อมูลจากที่ SAP กล่าวไว้, ระบบ ERP บูรณาการกระบวนการทางธุรกิจที่สำคัญ เช่น การเงิน ทรัพยากรบุคคล การผลิต ห่วงโซ่อุปทาน การบริการ การจัดซื้อจัดจ้าง และอื่นๆ เข้าสู่ระบบเดียวกัน ในตอนแรก ระบบ ERP เป็นเครื่องมือการจัดการพื้นฐาน แต่ได้พัฒนาเป็นแพลตฟอร์มขั้นสูงบนคลาวด์ที่ใช้ประโยชน์จาก AI และการเรียนรู้ของเครื่องเพื่อเพิ่มการทำงานอัตโนมัติและข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วยข้อมูล ระบบ ERP ทำหน้าที่เป็น “ระบบบันทึก” สำหรับองค์กร โดยให้ที่เก็บข้อมูลศูนย์กลางสำหรับข้อมูลทางธุรกิจทั้งหมด
วิวัฒนาการของ ERP: จากระบบเก่าสู่โซลูชันสมัยใหม่
ระบบ ERP ได้มีการพัฒนาอย่างมากในช่วงหลายปีที่ผ่านมา เปลี่ยนจากโซลูชันพื้นฐานที่มุ่งเน้นการผลิตไปสู่แพลตฟอร์มที่ครอบคลุมและบูรณาการซึ่งขับเคลื่อนประสิทธิภาพทางธุรกิจ ในตอนแรก แนวคิดนี้เริ่มต้นด้วยการวางแผนความต้องการวัสดุ (MRP) ซึ่งมุ่งเน้นไปที่การจัดการกระบวนการผลิตเป็นหลัก แนวทางนี้ขยายด้วยการวางแผนทรัพยากรการผลิต (MRP II) ซึ่งรวมฟังก์ชันการผลิตเพิ่มเติม ในช่วงปลายทศวรรษ 1990 ระบบเหล่านี้พัฒนาเป็นการวางแผนทรัพยากรองค์กร (ERP) ซึ่งบูรณาการฟังก์ชันทางธุรกิจที่หลากหลาย เช่น การเงิน ทรัพยากรบุคคล และการจัดการห่วงโซ่อุปทานเข้าสู่ระบบเดียวที่เป็นเอกภาพ
ในช่วงไม่กี่ปีที่ผ่านมา ระบบ ERP ยังคงพัฒนาต่อไป โดยรวมเทคโนโลยีที่เกิดขึ้นใหม่ เช่น ปัญญาประดิษฐ์ การเรียนรู้ของเครื่อง และเครื่องมือการเปลี่ยนแปลงทางดิจิทัลอื่นๆ เพื่อเพิ่มฟังก์ชันการทำงาน ปรับปรุงการตัดสินใจ และเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพกระบวนการทางธุรกิจ
ทำไม ERP จึงสำคัญ?
ระบบ ERP เป็นกระดูกสันหลังของการดำเนินธุรกิจ นำเสนอการทำงานอัตโนมัติ การบูรณาการ และข้อมูลเชิงลึกแบบเรียลไทม์ พวกมันมีความสำคัญในการปรับปรุงการดำเนินงาน ลดความเสี่ยง และช่วยให้ตัดสินใจได้เร็วขึ้น ซอฟต์แวร์บางแพ็คเกจถูกสร้างขึ้นเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์เฉพาะ ตัวอย่างเช่น ซอฟต์แวร์การจัดการสินค้าคงคลังใช้ในการรักษาสินค้าคงคลัง ซอฟต์แวร์ CRM (การจัดการความสัมพันธ์ลูกค้า) บันทึกรายละเอียดและการปฏิสัมพันธ์ของลูกค้า ซอฟต์แวร์บัญชีจัดการบันทึกและธุรกรรมทางการเงิน
ในทางกลับกัน ระบบ ERP จัดการฟังก์ชันธุรกิจหลักทั้งหมด – และรวมทั้งหมดไว้ในที่เดียว
สำหรับบทบาทต่างๆ ภายในบริษัท:
- การเงิน: ให้ข้อมูลทางการเงินแบบเรียลไทม์เพื่อการจัดทำงบประมาณและการคาดการณ์ที่ดีขึ้น
- การขาย: ปรับปรุงการจัดการความสัมพันธ์ลูกค้าและการติดตามการขาย
- โลจิสติกส์: เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการจัดการสินค้าคงคลังและประสิทธิภาพของห่วงโซ่อุปทาน
- การจัดการ: นำเสนอข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่ครอบคลุมสำหรับการวางแผนเชิงกลยุทธ์
ในสภาพแวดล้อมทางธุรกิจที่รวดเร็วในปัจจุบัน ความสำคัญของระบบ ERP ยังคงเติบโตอย่างต่อเนื่อง
ฟังก์ชันหลักของระบบ ERP มีอะไรบ้าง?
ERP บูรณาการฟังก์ชันทางธุรกิจที่สำคัญโดยใช้โมดูลต่างๆ ที่ตอบสนองแผนกต่างๆ โมดูลเหล่านี้ประกอบด้วย:
- การเงิน: จัดการบัญชี การจัดทำงบประมาณ และการรายงานทางการเงิน
- ทรัพยากรบุคคล (HR): จัดการข้อมูลพนักงาน การจ่ายเงินเดือน และการสรรหาบุคลากร
- การจัดการห่วงโซ่อุปทาน: ดูแลสินค้าคงคลัง การจัดซื้อจัดจ้าง และความสัมพันธ์กับผู้จำหน่าย
- การผลิต: อำนวยความสะดวกในการวางแผนการผลิต การควบคุมคุณภาพ และการบำรุงรักษา
- การขายและการตลาด: จัดการความสัมพันธ์ลูกค้า คำสั่งซื้อ และแคมเปญการตลาด
โมดูลเหล่านี้ทำงานร่วมกันเพื่อให้แหล่งข้อมูลที่เป็นหนึ่งเดียวกันในทุกแผนก ขจัดไซโลข้อมูลและรับรองความสอดคล้อง
วิธีการทำงานของ ERP
ในทางทฤษฎี การทำงานของซอฟต์แวร์ ERP นั้นเรียบง่าย เป็นระบบที่รวมกระบวนการทางธุรกิจของคุณให้เป็นหนึ่งเดียวโดยจัดเก็บข้อมูลทั้งหมดจากแผนกต่างๆ ไว้ในแพลตฟอร์มเดียว คุณสามารถปรับระดับการเข้าถึงของผู้ใช้ขึ้นอยู่กับอาวุโสหรือหน้าที่งาน เนื่องจากระบบมาพร้อมกับแดชบอร์ดที่ช่วยให้คุณปรับแต่งได้ตามกรณีการใช้งานของคุณ
ทุกแผนกป้อนข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบโดยใช้รูปแบบที่คุณกำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้า จากนั้นข้อมูลจะถูกเก็บไว้ในฐานข้อมูลส่วนกลางซึ่งระบบจะทำหน้าที่วิเคราะห์ ดังนั้น สมมติว่าผู้จัดการฝ่ายขายต้องการตรวจสอบคุณภาพของลูกค้าเป้าหมายจากทีมการตลาด เขาสามารถเข้าถึงข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวข้องได้ด้วยการคลิกเพียงไม่กี่ครั้ง หากฝ่ายทรัพยากรบุคคลต้องการรายงานเกี่ยวกับอัตราการเข้างานและการลาออก – ระบบจะช่วยสร้างรายงานเฉพาะที่พวกเขาต้องการ
เนื่องจากข้อมูลถูกนำมาจากแต่ละโมดูลและจัดเก็บไว้ในตำแหน่งกลาง จึงช่วยขจัดข้อผิดพลาดและข้อมูลซ้ำซ้อน นอกจากนี้ ซอฟต์แวร์ ERP ยังอนุญาตให้ใช้แอปบูรณาการจากบุคคลที่สามเพื่อช่วยให้กระบวนการทางธุรกิจของคุณราบรื่นยิ่งขึ้น
การสามารถเข้าถึงข้อมูลทั้งหมดและอัตราความคืบหน้าจากโมดูลและแดชบอร์ดที่เป็นหนึ่งเดียวเหล่านี้ ช่วยให้คุณและฝ่ายบริหารที่เหลือสามารถตัดสินใจทางธุรกิจอย่างชาญฉลาดและทำได้เร็วขึ้น
โมดูล ERP
ระบบ ERP ประกอบด้วยโมดูลต่างๆ ที่ทำงานร่วมกันโดยใช้ข้อมูลร่วมกัน โมดูลเหล่านี้ประกอบด้วย:
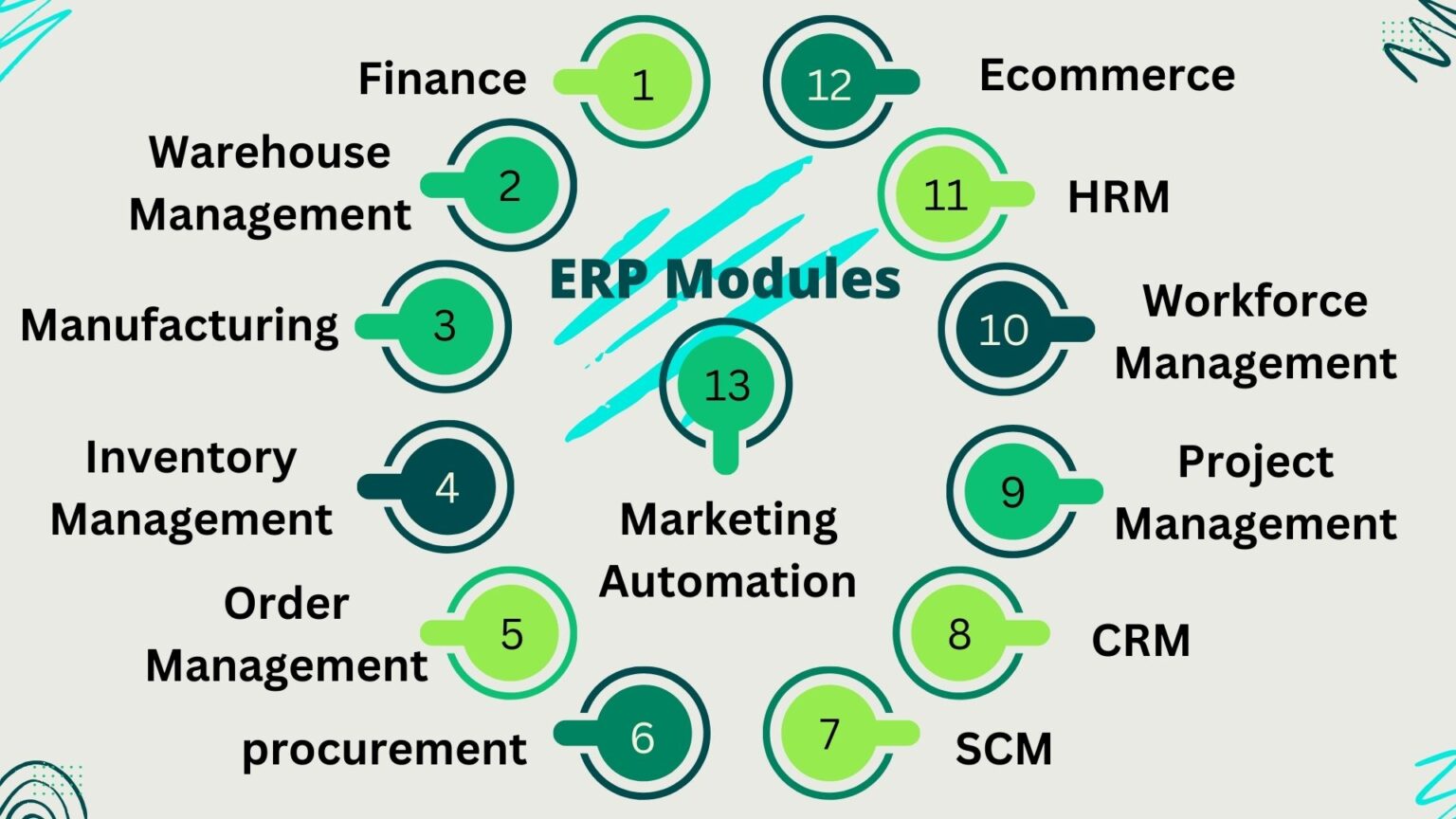
โมดูลเหล่านี้บูรณาการกันอย่างราบรื่น ช่วยให้ข้อมูลไหลเวียนระหว่างแผนกและให้มุมมองที่ครอบคลุมเกี่ยวกับการดำเนินงานทางธุรกิจ ระบบ ERP ยังสามารถบูรณาการกับระบบธุรกิจอื่นๆ เช่น การจัดการความสัมพันธ์ลูกค้า (CRM) การจัดการทุนมนุษย์ (HCM) และแพลตฟอร์มอีคอมเมิร์ซ ซึ่งช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและการทำงานร่วมกันโดยรวม
ประเภทของการนำ ERP ไปใช้
ซอฟต์แวร์ ERP สามารถนำไปใช้ได้หลายวิธี:
- ERP บนคลาวด์: โฮสต์บนคลาวด์ ใช้ระบบสมัครสมาชิก มีค่าใช้จ่ายเริ่มต้นต่ำ เหมาะสำหรับธุรกิจที่ต้องการความสามารถในการขยายตัวและความยืดหยุ่น
- ERP แบบติดตั้งในองค์กร: รูปแบบดั้งเดิม ติดตั้งในเซิร์ฟเวอร์ของบริษัท เหมาะสำหรับบริษัทที่มีความต้องการด้านความปลอดภัยและการปฏิบัติตามกฎระเบียบเฉพาะ
- ERP แบบไฮบริด: ผสมผสานฟังก์ชันการทำงานทั้งบนคลาวด์และแบบติดตั้งในองค์กร นำเสนอความยืดหยุ่นและการปรับแต่ง
ERP สำหรับอุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ
ซอฟต์แวร์ ERP มีความหลากหลายและสามารถปรับให้เข้ากับอุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ ได้ รวมถึง:
- สาธารณูปโภค: การจัดการสินทรัพย์และการคาดการณ์อะไหล่
- การผลิต: การวางแผนการผลิต การควบคุมคุณภาพ และการบูรณาการห่วงโซ่อุปทาน
- การค้าส่งและการจัดจำหน่าย: การจัดการสินค้าคงคลังและการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพด้านโลจิสติกส์
- บริการวิชาชีพ: การจัดการโครงการ การวางแผนทรัพยากร และการควบคุมทางการเงิน
- การค้าปลีก: การบูรณาการอีคอมเมิร์ซ การบริการลูกค้า และการซิงโครไนซ์สินค้าคงคลัง
วิธีบูรณาการระบบ ERP
การบูรณาการซอฟต์แวร์ ERP กับแอปพลิเคชันทางธุรกิจอื่นๆ เกี่ยวข้องกับวิธีการต่างๆ รวมถึงการใช้ API (Application Programming Interfaces), iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) และตัวเชื่อมต่อแบบกำหนดเอง การบูรณาการที่มีประสิทธิภาพช่วยให้การดำเนินงานราบรื่น ลดการป้อนข้อมูลด้วยตนเอง และสร้างสภาพแวดล้อมข้อมูลที่เป็นหนึ่งเดียว
แนวทางการเชื่อมต่อนี้ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพโดยรวมด้วยการให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่ครอบคลุมในทุกฟังก์ชันทางธุรกิจ และอำนวยความสะดวกในการสื่อสารและการแบ่งปันข้อมูลระหว่างแผนกที่ดีขึ้น ในฐานะศูนย์กลาง ระบบ ERP ช่วยให้มั่นใจว่าการดำเนินงานจะราบรื่นและรักษาความสอดคล้องของข้อมูลในทุกแอปพลิเคชันที่เชื่อมต่อ
ERP บนคลาวด์คืออะไร?
ERP บนคลาวด์ หรือที่รู้จักกันในชื่อ SaaS (Software as a Service) ERP ยังคงเป็นการวางแผนทรัพยากรองค์กรเช่นเดิม แต่ส่งมอบผ่านคลาวด์ แทนที่จะต้องใช้เซิร์ฟเวอร์และอุปกรณ์เฉพาะเพื่อเรียกใช้ระบบ เหมือนกับกรณีของระบบ ERP แบบติดตั้งในองค์กรแบบดั้งเดิม นี่เป็นปัจจัยสำคัญที่ทำให้ ERP เข้าถึงได้ง่ายขึ้นสำหรับตลาด SMB นอกจากนี้ยังช่วยเร่งการนำไปใช้และการส่งมอบ ERP ซึ่งมักเป็นปัจจัยขับเคลื่อนหลักสำหรับธุรกิจขนาดใหญ่
ประโยชน์ของ ERP บนคลาวด์สำหรับ SMB
ประโยชน์ทันทีบางประการที่โซลูชัน ERP บนคลาวด์สำหรับ SMB มอบให้ ได้แก่:
- ใช้ประโยชน์จากกระบวนการที่เป็นแนวปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดเพื่อปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพ
- ให้ธุรกิจใช้ข้อมูลแหล่งเดียว
- ลดต้นทุนผ่านการทำงานอัตโนมัติ
- สร้างประสบการณ์ลูกค้าที่สอดคล้องกันมากขึ้น
- แดชบอร์ดและ KPI เพื่อดูตำแหน่งทางธุรกิจได้อย่างรวดเร็ว
สำหรับธุรกิจขนาดเล็ก ERP บนคลาวด์สามารถช่วยกำหนดกระบวนการที่เป็นแนวปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดเช่นเดียวกับที่องค์กรระดับองค์กรใช้อยู่
เนื่องจากมีตัวเลือกซอฟต์แวร์บนคลาวด์จำนวนมาก จึงควรวิจัยตัวเลือกและติดต่อรายชื่อผู้ให้บริการโซลูชันที่คัดเลือกไว้เมื่อคุณพร้อมที่จะเข้าใจว่าระบบใดจะเหมาะสมที่สุดกับความต้องการทางธุรกิจเฉพาะของคุณ
สำหรับธุรกิจขนาดเล็ก ERP บนคลาวด์สามารถช่วยกำหนดกระบวนการที่เป็นแนวปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดเช่นเดียวกับที่องค์กรระดับองค์กรใช้อยู่
ประโยชน์ของ ERP บนคลาวด์สำหรับธุรกิจขนาดใหญ่
ประโยชน์บางประการที่โซลูชัน ERP ระดับองค์กรมอบให้ ได้แก่:
- เพิ่มผลกำไรโดยรวม
- การปฏิบัติตามกฎระเบียบและการจัดการความเสี่ยงที่แข็งแกร่ง
- การจัดการโครงการที่ดีขึ้น
- เพิ่มการมองเห็นและการทำงานร่วมกันระหว่างแผนก
- แดชบอร์ดและ KPI เพื่อดูประสิทธิภาพของแผนกและธุรกิจโดยรวม
มีรุ่นเฉพาะอุตสาหกรรมสำหรับส่วนต่างๆ เช่น การจัดจำหน่ายสินค้าส่ง การผลิต การค้าปลีก และอื่นๆ อีกมากมาย
ตัวอย่างของโซลูชัน ERP บนคลาวด์ในการทำงาน
ลองจินตนาการถึงสถานการณ์ที่ลูกค้าสร้างการสอบถามเพื่อสั่งซื้อสินค้าจำนวนมาก รายละเอียดทั้งหมดจากการสอบถามนี้จะถูกส่งและซิงโครไนซ์กับคลังสินค้า สินค้าคงคลัง การผลิต และการจัดส่งทันที เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าบริษัทของคุณสามารถจัดการคำสั่งซื้อได้
สิ่งนี้ยังถูกซิงโครไนซ์และตรวจสอบประมาณการภาษี เพื่อให้ราคาคำสั่งซื้อถูกคำนวณ ใบแจ้งหนี้ถูกสร้างขึ้นตามการคำนวณเหล่านี้ ซึ่งทีมขายสามารถส่งต่อให้ลูกค้าได้
หากลูกค้าเลือกที่จะดำเนินการสั่งซื้อจำนวนมาก รายการโดยละเอียดของวัสดุ กิจกรรม และกำลังคนที่เกี่ยวข้องจะถูกส่งไปยังทีมที่เกี่ยวข้องทันทีผ่านแดชบอร์ดหรือโมดูลระบบของแต่ละทีม
กระบวนการทั้งหมดสามารถเข้าถึงและตรวจสอบได้ และอนุญาตให้มีการปรับเปลี่ยนที่จำเป็นเพื่อให้การผลิต การจัดการ และการจัดส่งเป็นไปตามแผน รายงานความคืบหน้าสามารถจัดทำได้หากธุรกิจของคุณต้องการ
12 คุณสมบัติและประโยชน์หลักของระบบ ERP
- การบูรณาการ
- การทำงานอัตโนมัติ
- การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล
- การรายงาน
- การติดตามและการมองเห็น
- การบัญชี
- การจัดการทางการเงิน
- การจัดการความสัมพันธ์ลูกค้า (CRM)
- การขายและการตลาด
- ทรัพยากรบุคคล (HR)
- การจัดการห่วงโซ่อุปทาน (SCM)
- การผลิต
คุณต้องการโซลูชัน ERP หรือไม่?
หากคุณต้องการขยายธุรกิจของคุณ สร้างฐานความรู้ที่แข็งแกร่ง และปรับปรุงกระบวนการทางธุรกิจหลักของคุณ คำตอบคือใช่ – คุณต้องการโซลูชัน ERP
การนำระบบ ERP ไปใช้ไม่ได้หมายความว่าคุณจะต้องมีกองทัพมืออาชีพด้านไอทีมาที่สำนักงานของคุณและเข้าควบคุมการดำเนินงานของคุณ โซลูชัน ERP บนคลาวด์ไม่ต้องการการเปลี่ยนแปลงฮาร์ดแวร์ที่มีอยู่ของคุณ หากคุณมีการเชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตที่เชื่อถือได้ คุณเพียงแค่เข้าสู่ระบบและสามารถเข้าถึงระบบ ERP ของคุณได้ไม่ว่าคุณจะอยู่ที่ไหน
โดยไม่ต้องติดตั้งในสถานที่ และมีความยืดหยุ่นในการเลือกโมดูลและคุณสมบัติที่ธุรกิจของคุณต้องการ โซลูชัน ERP จึงไม่มีค่าใช้จ่ายสูงอย่างที่คุณอาจคิดในตอนแรก แม้ว่าคุณจะไม่เห็นช่องทางในการปรับปรุงการดำเนินงานของคุณและคิดว่าคุณไม่ต้องการ ERP ในตอนนี้ แต่มีโอกาสสูงที่คู่แข่งทางธุรกิจของคุณกำลังใช้งานอยู่แล้ว ดังนั้น หากคุณต้องการรักษาความสามารถในการแข่งขัน คุณต้องแน่ใจว่าคุณกำลังใช้เครื่องมือที่เหมาะสม
5 สัญญาณที่แน่ชัดว่าบริษัทของคุณต้องการโซลูชัน ERP
ไม่มีใครบอกว่าโซลูชัน ERP จะแก้ปัญหาความท้าทายทางธุรกิจทั้งหมดของคุณ แต่มันจะช่วยให้การดำเนินงานประจำวันของคุณมีเสถียรภาพและช่วยให้คุณมุ่งเน้นไปที่การเติบโตของธุรกิจของคุณได้มากขึ้น
นี่คือห้าตัวบ่งชี้สำคัญที่คุณต้องนำระบบ ERP มาใช้สำหรับบริษัทของคุณ:
- คุณกำลังประสบกับข้อผิดพลาดในกระแสเงินสดจำนวนมาก เป็นเรื่องยากที่จะเข้าใจการไหลของเงินเพราะคุณกำลังใช้สเปรดชีตที่แตกต่างกันเพื่อ “ติดตาม” กระแสเงินสด
- คุณใช้ซอฟต์แวร์ประเภทต่างๆ สำหรับกระบวนการธุรกิจหลักทุกอย่าง การใช้ซอฟต์แวร์ที่แตกต่างกันสามารถสร้างไซโลและปัญหาภายในกระบวนการทางธุรกิจของคุณ
- คุณกำลังทำการติดตามการขายด้วยตนเองและพึ่งพารายงานกระดาษมากเกินไปสำหรับการอัปเดตยอดขาย
- คุณกำลังใช้เงินและเวลาจำนวนมากในการอัปเกรดและบำรุงรักษาไอที
- คุณไม่มีข้อมูลที่ถูกต้องเกี่ยวกับความสามารถในการทำกำไรของธุรกิจของคุณ
แนวปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดในการนำ ERP ไปใช้
จัดตั้งทีมโครงการที่แข็งแกร่ง
นี่เป็นขั้นตอนแรกเมื่อนำโซลูชัน ERP ไปใช้ โดยปกติ ทีมโครงการจะประกอบด้วยผู้จัดการโครงการที่ทุ่มเท และตัวแทนจากกลุ่มธุรกิจต่างๆ ในโครงการ ผู้จัดการโครงการจะรับผิดชอบในการปรับ จัดลำดับความสำคัญ และจัดเรียงทรัพยากรตามความต้องการของการนำไปใช้
เลือกวิธีการที่เหมาะสม
การเลือกวิธีที่ดีที่สุดในการนำซอฟต์แวร์ ERP ไปใช้เป็นสิ่งจำเป็นในความสำเร็จโดยรวมของการนำไปใช้
ใช้เวลาในการฝึกอบรม
การตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าพนักงานของคุณได้รับการฝึกอบรมที่เหมาะสมเกี่ยวกับวิธีการใช้ระบบช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพโดยรวม การนำไปใช้ที่เร็วขึ้น ซึ่งช่วยให้ได้รับผลตอบแทนจากการลงทุน (ROI) จากซอฟต์แวร์เร็วขึ้น
การโยกย้ายข้อมูล
การโยกย้ายข้อมูลไปยังแพลตฟอร์ม ERP เป็นเรื่องยากในระหว่างการนำไปใช้ เนื่องจากมีความเสี่ยงที่จะสูญเสียข้อมูลเมื่อรวมข้อมูลจากแอปพลิเคชันต่างๆ
ต้นทุนรวมของการนำ ERP ไปใช้
ต้นทุนของการนำ ERP ไปใช้อาจแตกต่างกันไปขึ้นอยู่กับปัจจัยหลายประการ ได้แก่:
- โมดูลที่ต้องการ: โมดูลที่มากขึ้นมักหมายถึงต้นทุนที่สูงขึ้น
- ประเภทการนำไปใช้: โซลูชันบนคลาวด์มีต้นทุนเริ่มต้นที่ต่ำกว่า แต่มีค่าธรรมเนียมการสมัครสมาชิกระยะยาวที่สูงกว่า ในขณะที่โซลูชันแบบติดตั้งในองค์กรมีต้นทุนเริ่มต้นที่สูงกว่า แต่มีค่าธรรมเนียมต่อเนื่องที่ต่ำกว่า
- การกำหนดราคาของผู้ขาย: ผู้ขายต่างๆ เสนอรูปแบบการกำหนดราคาที่แตกต่างกัน
- ต้นทุนเพิ่มเติมที่ควรพิจารณา: ได้แก่ ค่าใช้จ่ายการฝึกอบรม ค่าการบำรุงรักษา และค่าการปรับแต่ง
มูลค่าทางธุรกิจของ ERP: การเพิ่มผลลัพธ์ทางธุรกิจและการลดต้นทุน
การนำระบบ ERP มาใช้ในภูมิทัศน์ทางธุรกิจที่มีการแข่งขันสูงในปัจจุบันมีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งสำหรับบริษัทที่ต้องการประสบกับการดำเนินงานที่มีประสิทธิภาพ ประสิทธิภาพที่เพิ่มขึ้น และความสำเร็จโดยรวม การนำโซลูชัน ERP ไปใช้ช่วยรวมศูนย์ข้อมูลและกระบวนการขององค์กร ช่วยให้องค์กรสามารถประสานงานระหว่างแผนกและเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพขั้นตอนการทำงาน ซึ่งส่งผลให้ประหยัดต้นทุนและเพิ่มรายได้
ข้อได้เปรียบหลักของระบบ ERP ประกอบด้วย:
- ข้อมูลเชิงลึกแบบเรียลไทม์: การรายงานที่ครอบคลุมให้ข้อมูลที่ถูกต้องและทันสมัยสำหรับการวางแผนกลยุทธ์อย่างมีข้อมูล
- ลดต้นทุนการดำเนินงาน: กระบวนการทางธุรกิจที่มีประสิทธิภาพและแนวปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดนำไปสู่การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของทรัพยากร
- การทำงานร่วมกันที่ดีขึ้น: การแบ่งปันข้อมูลสำคัญที่เกี่ยวข้องกับสัญญา การขอซื้อ และคำสั่งซื้อระหว่างผู้ใช้อย่างราบรื่น
- ประสิทธิภาพที่ดีขึ้น: ประสบการณ์ผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันในหลายฟังก์ชันทางธุรกิจและสภาพแวดล้อมการทำงานที่มีโครงสร้างที่ดี
- โครงสร้างพื้นฐานที่เป็นแบบเดียวกัน: รูปลักษณ์และความรู้สึกที่มีประสิทธิภาพตั้งแต่งานสำนักงานหลังบ้านไปจนถึงกิจกรรมสำนักงานหน้าบ้าน
- การยอมรับของผู้ใช้ที่สูงขึ้น: ประสบการณ์ผู้ใช้ที่เป็นเอกภาพส่งเสริมการยอมรับอย่างกว้างขวางทั่วทั้งองค์กร
- การลดความเสี่ยง: ความถูกต้องของข้อมูลที่ดีขึ้นและการควบคุมทางการเงินที่แข็งแกร่งช่วยให้มั่นใจในความมั่นคงทางธุรกิจ
- การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพต้นทุน: ระบบที่เป็นแบบเดียวกันและบูรณาการช่วยลดต้นทุนในการจัดการและการดำเนินงาน
การนำโซลูชัน ERP ไปใช้ช่วยให้ธุรกิจสามารถวางตำแหน่งตนเองให้มีความคล่องตัวและประสบความสำเร็จในระยะยาว
แนวโน้มในอนาคตของ ERP: อะไรคือสิ่งที่จะเกิดขึ้นต่อไป?
Stephen Canning ซีอีโอของ JCurve Solutions (ASX: JCS) เน้นย้ำถึงประโยชน์ของระบบ ERP โดยเน้นว่าพวกมันนำเสนอโซลูชันที่เป็นหนึ่งเดียวสำหรับฟังก์ชันธุรกิจหลัก ตามที่ Canning กล่าว “มันเป็นโซลูชันที่เป็นเอกภาพเดียวกันด้วยแหล่งข้อมูลเดียว ส่งมอบประสิทธิภาพในการดำเนินงานและช่วยให้ธุรกิจสามารถดำเนินการได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลา – แม้แต่จากอุปกรณ์มือถือในต่างประเทศ ด้วย ERP เจ้าของธุรกิจและผู้จัดการสามารถติดตามประสิทธิภาพผ่านแดชบอร์ดธุรกิจได้อย่างง่ายดาย ช่วยให้พวกเขาดำเนินธุรกิจได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพและมั่นใจ”
อนาคตของระบบ ERP กำลังถูกกำหนดรูปร่างโดยแนวโน้มสำคัญหลายประการที่ขับเคลื่อนวิวัฒนาการและผลกระทบต่อธุรกิจ:
- การยอมรับคลาวด์: การเปลี่ยนไปใช้โซลูชัน ERP บนคลาวด์ยังคงเติบโตอย่างต่อเนื่อง เนื่องจากธุรกิจต่างๆ มองหาความสามารถในการขยายตัว ความยืดหยุ่น และการลดค่าใช้จ่ายด้านไอทีที่สูง
- การบูรณาการแนวตั้ง: ผู้ให้บริการ ERP มุ่งเน้นไปที่ฟังก์ชันการทำงานเฉพาะอุตสาหกรรมมากขึ้น โดยนำเสนอโซลูชันที่ปรับแต่งเพื่อตอบสนองความต้องการเฉพาะของแต่ละภาคส่วน
- การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพประสบการณ์ผู้ใช้: ซอฟต์แวร์ ERP สมัยใหม่กำลังเพิ่มประสบการณ์ผู้ใช้ผ่านแดชบอร์ดที่ปรับแต่งได้ ข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วย AI และแพลตฟอร์ม low-code ทำให้พวกมันใช้งานง่ายและปรับตัวได้มากขึ้น
การเริ่มต้นเส้นทาง ERP ของคุณกับ Jcurve
ประโยชน์ของ Jcurve ERP มีมากมาย ทำให้เป็นจุดเริ่มต้นที่เหมาะสำหรับธุรกิจขนาดเล็กที่กำลังเริ่มต้นเส้นทาง ERP ในฐานะแพลตฟอร์มบนคลาวด์ที่ปรับขนาดได้ Jcurve ERP ปรับตัวตามความต้องการที่เปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์กรของคุณ ครอบคลุมฟังก์ชันการทำงานหลักที่พบในระบบ ERP ขนาดใหญ่ เช่น การบัญชีและการเงิน การขายและการตลาด และการจัดการสินค้าคงคลัง ในขณะที่ตอบสนองความต้องการของธุรกิจขนาดเล็กโดยเฉพาะ
การใช้ประโยชน์จาก Jcurve ERP ช่วยให้คุณเข้าถึงข้อมูลที่ทันสมัยเกี่ยวกับบริษัทของคุณ ช่วยให้คุณสามารถตัดสินใจได้อย่างรวดเร็วและชาญฉลาดเพื่อความสำเร็จอย่างต่อเนื่อง
บทสรุป
โดยสรุป ระบบ ERP เป็นเครื่องมือที่จำเป็นอย่างยิ่งสำหรับธุรกิจสมัยใหม่ โดยบูรณาการฟังก์ชันที่สำคัญเข้าสู่ระบบเดียวที่เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ ความถูกต้องของข้อมูล และการตัดสินใจ เมื่อเทคโนโลยี ERP ยังคงพัฒนาต่อไป ธุรกิจต่างๆ สามารถคาดหวังระดับการทำงานอัตโนมัติ การบูรณาการ และข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วยข้อมูลที่สูงขึ้นได้
สำหรับผู้ที่สนใจศึกษาเพิ่มเติม หัวข้อต่างๆ เช่น ERP เทียบกับ CRM กรณีศึกษาเฉพาะอุตสาหกรรม และผลกระทบของ AI ต่อระบบ ERP ให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่มีค่าเกี่ยวกับอนาคตของการวางแผนทรัพยากรองค์กร
การนำระบบ ERP ไปใช้อาจเป็นการลงทุนที่สำคัญ แต่ผลตอบแทนในด้านประสิทธิภาพการดำเนินงาน ความแม่นยำของข้อมูล และความสามารถในการแข่งขันโดยรวมสามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงเกมสำหรับองค์กรได้ เมื่อธุรกิจเติบโตและซับซ้อนมากขึ้น ความสำคัญของการมีระบบ ERP ที่แข็งแกร่งและปรับขนาดได้จะยิ่งเพิ่มมากขึ้น
ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็นธุรกิจขนาดเล็กที่กำลังพิจารณาการเริ่มต้นด้วยโซลูชันเช่น Jcurve ERP หรือองค์กรขนาดใหญ่ที่กำลังมองหาระบบที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้นเช่น NetSuite ERP การลงทุนในเทคโนโลยี ERP ที่เหมาะสมสามารถเป็นก้าวสำคัญสู่การเติบโตและความสำเร็จในระยะยาว

Jessica has a Bachelor of Arts degree from Trent University and a Masters degree from Cambridge University. He is an Adjunct Professor of Finance at Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business and is both a Canadian Chartered Professional Accountant and a UK Chartered Accountant.

Jessica has a Bachelor of Arts degree from Trent University and a Masters degree from Cambridge University. He is an Adjunct Professor of Finance at Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business and is both a Canadian Chartered Professional Accountant and a UK Chartered Accountant.





